What Is College Funding?
College education is a significant expenditure for most consumers. Recent statistics show that the average student loan debt is $46,459 per person1. For the 2020-2021 school year, a public four-year degree from an in-state institution costs almost $90,000 on average including room and board2.
Without proper planning, the cost of higher education can become a heavy financial burden that trails college graduates for years, even decades.
Keep reading this blog or skip to our college funding video below from AllGen Academy.
Is College Worth It?
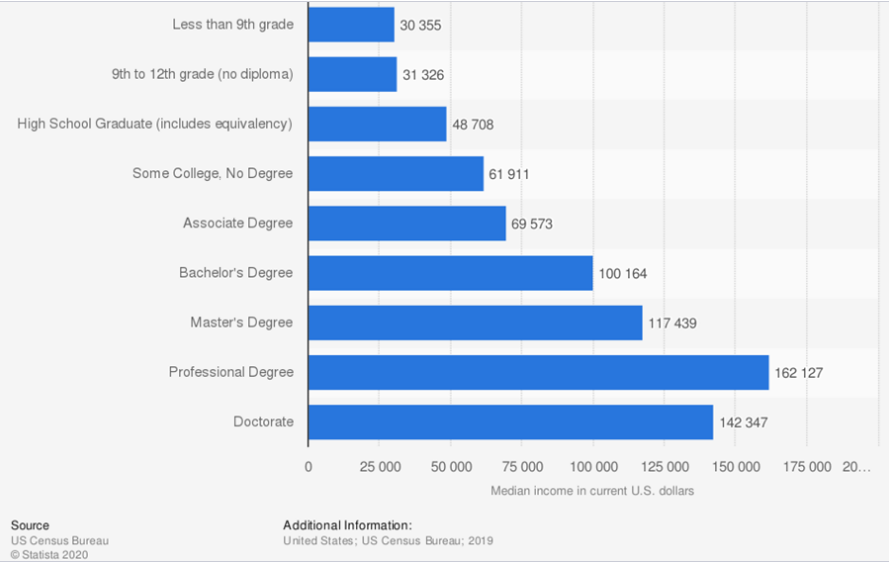
The following graph by the US Census Bureau shows that in general, higher education does result in higher earnings. Each additional level of education correlates to a higher income level up until professional degrees.
However, note that these are median incomes. Different people will experience varying levels of success in income earning and career progression that does not always fit their education level. Lastly, many people succeed in life without any higher education so not going to college could also be a viable option.
Ways to Pay for College
Regardless of the education level that you or your child aspires to, the goal is to graduate with no debt. You can achieve this using one or a combination of these methods:
- Scholarships
- Grants
- Savings
- Working
When it comes to college savings, there are multiple types of vehicles that you can use. Here is a list of the most common types.
Prepaid 529
A common choice for college funding is the prepaid 529 plan. This type of plan allows parents to purchase college credit hours at today’s rate for use when the child attends college in the future.
The biggest advantage to prepaid plans is that you essentially ‘lock in’ discounted tuition rates today instead of paying for the inflated cost in the future. As you may know, college costs have risen dramatically in recent history with annual inflation rates between 5-7%. Tuition increases have started to flatten in the past couple of years to 3-4% annually. Even at the lower inflation rate, it’s still beneficial to ‘prepay’ for college tuition at today’s prices versus waiting to pay a higher cost in the future.
Prepaid 529 plans are suitable for shorter time frames when a child will be entering college in the near future. There is not as much time for investments to grow and compound so it may be more advantageous to prepay for tuition versus investing for just a few years. However only 12 states currently offer prepaid 529 plans.
Here are some additional pros and cons of prepaid 529 plans.
529 Savings Account
Another popular choice is the 529 savings plan which is a tax advantaged investment account for education expenses. Parents, grandparents, or other relatives/friends can open a 529 savings account for the benefit of a future college student and make unlimited contributions into the account.
Savings are invested according to the time horizon of when the funds will be needed. Investments grow tax deferred and withdrawals that are used for qualified education expenses are tax free. In recent years, the IRS has broadened the definition of qualified expenses to include K-12 tuition, homeschool expenses, and even some student loan repayment. Nonqualified withdrawals are taxed and subject to a 10% penalty.
Contributions into a 529 account may also qualify for state income tax credit depending on the state where the grantor (parent, grandparent, relative, etc.) resides. However, if contributions exceed the annual gift tax exclusion amount ($15,000 in 2021), the gift will need to be reported on a gift tax return and may incur federal gift tax.
Coverdell Education Savings Account
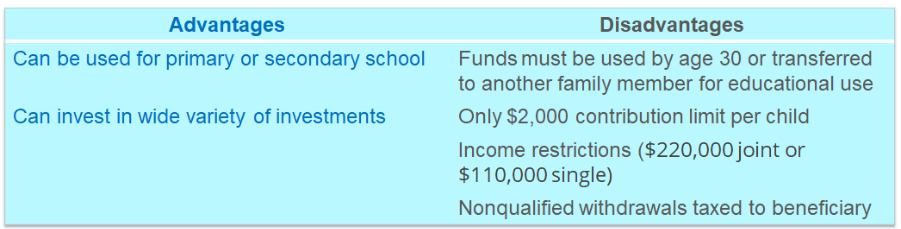
A Coverdell Education Savings Account (ESA) is a tax deferred trust account for minors to cover education expenses. ESAs can be used for qualified primary or secondary education regardless of the type of school. They can also be invested in a wide variety of investments as opposed to 529 savings plans which are typically more limited in investment options.
Some drawbacks are that funds need to be used by the beneficiary by age 30 or transferred to another family member for educational use. The annual contribution limit is only $2,000 per child and there are income restrictions on who can contribute (up to $220,000 married filing jointly or $110,000 single in 2021). Like the 529 savings plan, nonqualified withdrawals are taxed and subject to a 10% penalty.
What If It Is Too Late to Save?
If you haven’t planned ahead and you or your child is starting college soon, there may be other ways to pay for school without incurring student loan debt:
- Many employers will pay for a portion or all of your schooling. If you work for certain organizations such as a university or the military, there may tuition benefits to you, your spouse, or children.
- Studies show that those who work part time through college have higher GPAs than those who don’t work.
- Look for scholarships and grants to supplement tuition costs.
Again, the goal is to graduate without student loan debt. College funding may seem daunting but planning ahead and doing your research can help you be better prepared.
Visit our next blog to download our College Funding Calculator! It will help you determine how much you need to start saving towards your/your child’s college education.
For more information on college funding, watch our AllGen Academy video below.
Sources:
1. Anna, H. (2021, May 20). How Many Americans Have Student Loan Debt? . Nerd Wallet. https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/loans/student-loans/how-many-americans-have-student-loan-debt.
This is the average total student loans of those who have student loans.
2. Ma, J., Pender, M., & Libassi, C. J. (2020, October). Trends in College Pricing and Student Aid 2020 . CollegeBoard. https://research.collegeboard.org/trends/college-pricing.
From Table CP-1. Calculated using 2020/21 rates over 4 years at 1% inflation.
Important Disclosures: The information provided here is of a general nature and is not intended to answer any individual’s financial questions. Do not rely on information presented herein to address your individual financial concerns. Your receipt of information from this material does not create a client relationship and the financial privileges inherent therein. If you have a financial question, you should consult an experienced financial advisor. Moreover, the hiring of a financial advisor is an important decision that should not be based solely upon blogs, articles, or advertisements. Before you hire a financial advisor, you should request information about the financial advisor’s qualifications and experiences. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. All expressions of opinion are subject to change without notice in reaction to shifting market conditions. Data contained herein from third party providers is obtained from what are considered reliable sources. However, its accuracy, completeness or reliability cannot be guaranteed. Examples provided are for illustrative (or “informational”) purposes only and not intended to be reflective of results you can expect to achieve. AllGen Financial Advisors, Inc. (AllGen) is an investment advisor registered with the SEC. AllGen does not provide personal financial advice via this material. The purpose of this material is limited to the dissemination of general information regarding the services offered by AllGen. The Disclosure Brochure, Form ADV Part II, which details business practices, services offered, and related fees of AllGen, is available upon request.